Posts for Tag: taxes
Understanding Tax Brackets: Interactive Income Tax Visualization and Calculator
Please check out the newer version of this visualization
How is your income distributed across tax brackets?
I previously made a graphical visualization of income and marginal tax rates to show how tax brackets work. That graph tried to show alot of info on the same graph, i.e. the breakdown of income tax brackets for incomes ranging from $10,000 to $3,000,000. It was nice looking, but I think several people were confused about how to read the graph. This Sankey graph is a more detailed look at the tax breakdown for one specific income. You can enter your (or any other) profile and see how taxes are distributed across the different brackets. It can help (as the other tried) to better understand marginal and average tax rates. This tool only looks at US Federal Income taxes and ignores state, local and Social Security/Medicare taxes.
– Use this button to generate a URL that you can share a specific set of inputs and graphs. Just copy the URL in the address bar at the top of your browser (after pressing the button).
Instructions for using the visual tax calculator:
- Select filing status: Single, Married Filing Jointly or Head of Household. For more info on these filing categories see the IRS website
- Enter your regular income and capital gains income. Regular income is wage or employment income and is taxed at a higher rate than capital gains income. Capital gains income is typically investment income from the sale of stocks or dividends and taxed at a lower rate than regular income.
- Move your cursor or click on the Sankey graph to select a specific link. This will give you more information about how income in a specific tax bracket is being taxed.
**Click Here to view other financial-related tools and data visualizations from engaging-data**
As seen with the marginal rates graph, there is a big difference in how regular income and capital gains are taxed. Capital gains are taxed at a lower rate and generally have larger bracket sizes. Generally, wealthier households earn a greater fraction of their income from capital gains and as a result of the lower tax rates on capital gains, these household pay a lower effective tax rate than those making an order of magnitude less in overall income.
Tax Brackets By Year
This table lets you choose to view the thresholds for each income and capital gains tax bracket for the last few years. You can see that tax rates are much lower for capital gains in the table below than for regular income.
For those not visually inclined, here is a written description of how to apply marginal tax rates. The first thing to note is that the income shown here in the graphs is taxable income, which simply speaking is your gross income with deductions removed. The standard deduction for 2018 range from $12,000 for Single filers to $24,000 for Married filers.
- If you are single, all of your regular taxable income between 0 and $9,525 is taxed at a 10% rate. This means that your all of your gross income below $12,000 is not taxed and your gross income between $12,000 and $21,525 is taxed at 10%.
- If you have more income, you move up a marginal tax bracket. Any taxable income in excess of $9,525 but below $38,700 will be taxed at the 12% rate. It is important to note that not all of your income is taxed at the marginal rate, just the income between these amounts.
- Income between $38,700 and $82,500 is taxed at 24% and so on until you have income over $500,000 and are in the 37% marginal tax rate . . .
- Thus, different parts of your income are taxed at different rates and you can calculate an average or effective rate (which is shown in the summary table).
- Capital gains income complicates things slightly as it is taxed after regular income. Thus any amount of capital gains taxes you make are taxed at a rate that corresponds to starting after you regular income. If you made $100,000 in regular income, and only $100 in capital gains income, that $100 dollars would be taxed at the 15% rate and not at the 0% rate, because the $100,000 in regular income pushes you into the 2nd marginal tax bracket for capital gains (between $38,700 and $426,700).
Data and Tools:
Tax brackets and rates were obtained from the IRS website and calculations were made using javascript and code modified from the Sankeymatic plotting website.
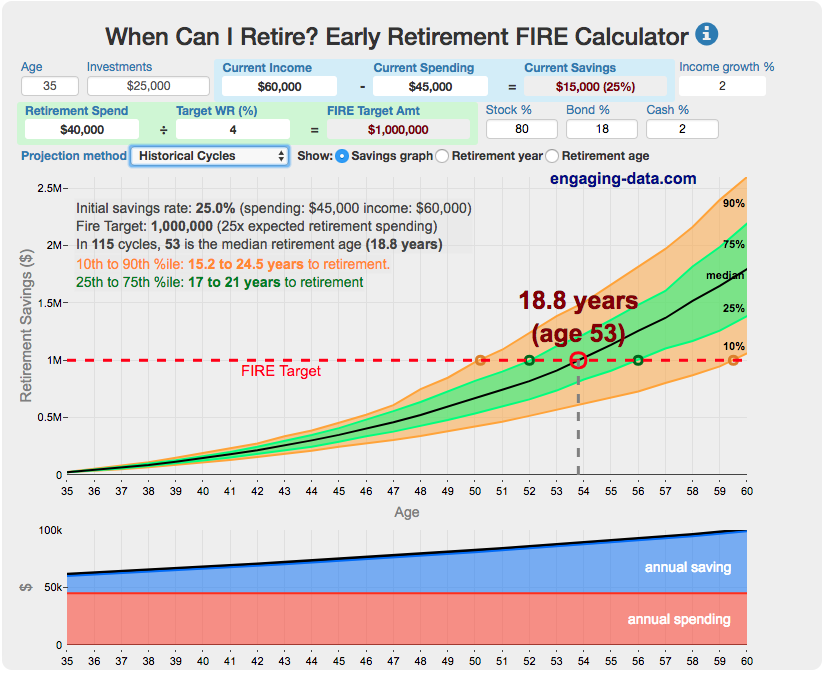
Early Retirement Calculators and Tools
Interested in Early Retirement or FIRE (Financial Independence to Retire Early)?
Here are some interactive and educational planning tools that I developed to help you understand the concepts of FIRE and calculate how long it will take to achieve retirement and how likely you are to survive retirement. Click on the tools below to try them out.
Financial Independence Calculators
Regardless of where you are on your path to FIRE, there are several types of tools that are useful:
Planning to get to retirement
How long and how safe will your retirement be?
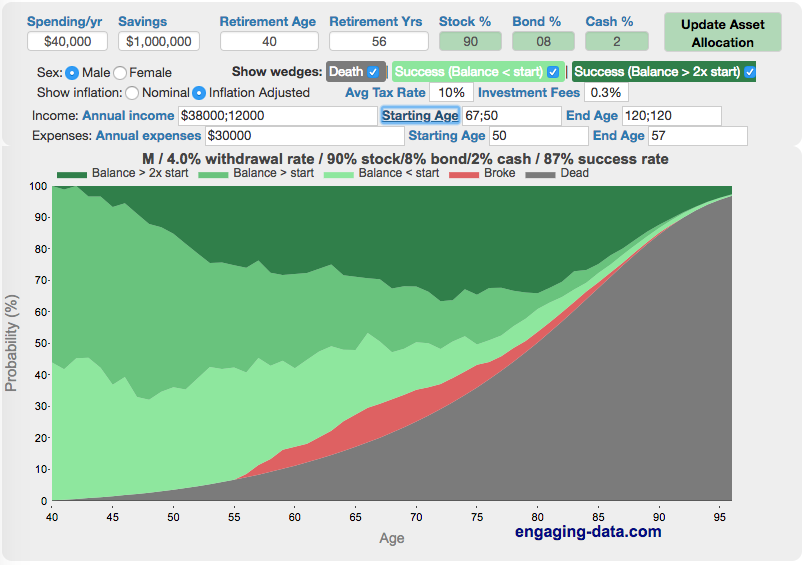
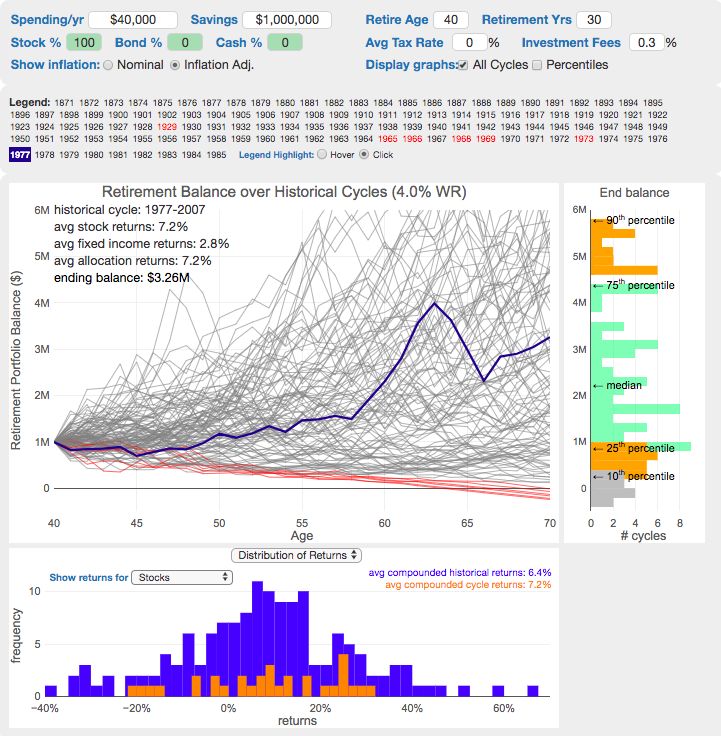
Rich, Broke or Dead? Will your Money Last Through Early Retirement?
Simulating retirement portfolio survival probability and human longevity
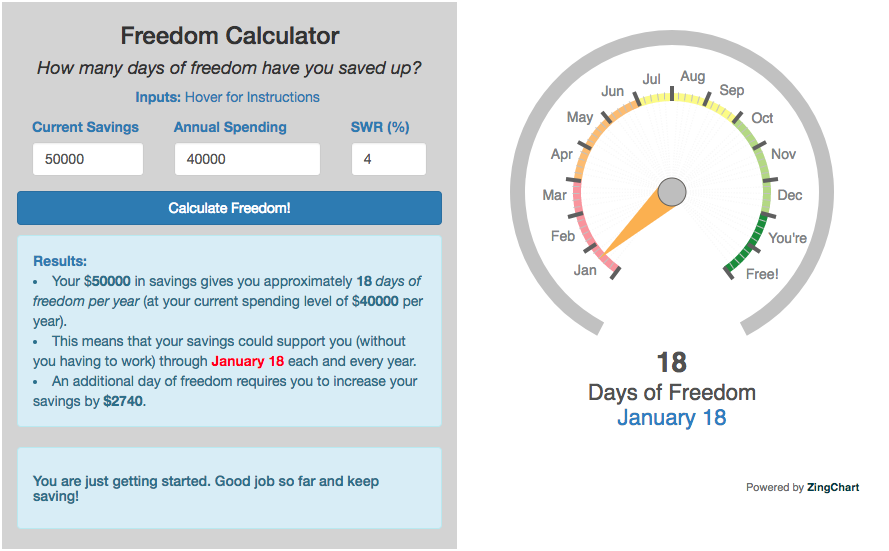
These tools all focus on the concept of FIRE. FIRE is the concept that revolves around saving and investing to achieve Financial Independence (FI) and to potentially Retire Early (RE). One of the core concepts is that once you can save up enough money, you can retire by withdrawing a fraction of this money annually to cover your living expenses. Other important topics related to this core concept have to do with reducing spending so you can save money and investing so your money can grow and sustain your retirement over many decades.
Other visualizations and tools related to Financial Independence
These tools relate to taxes and stock market returns.
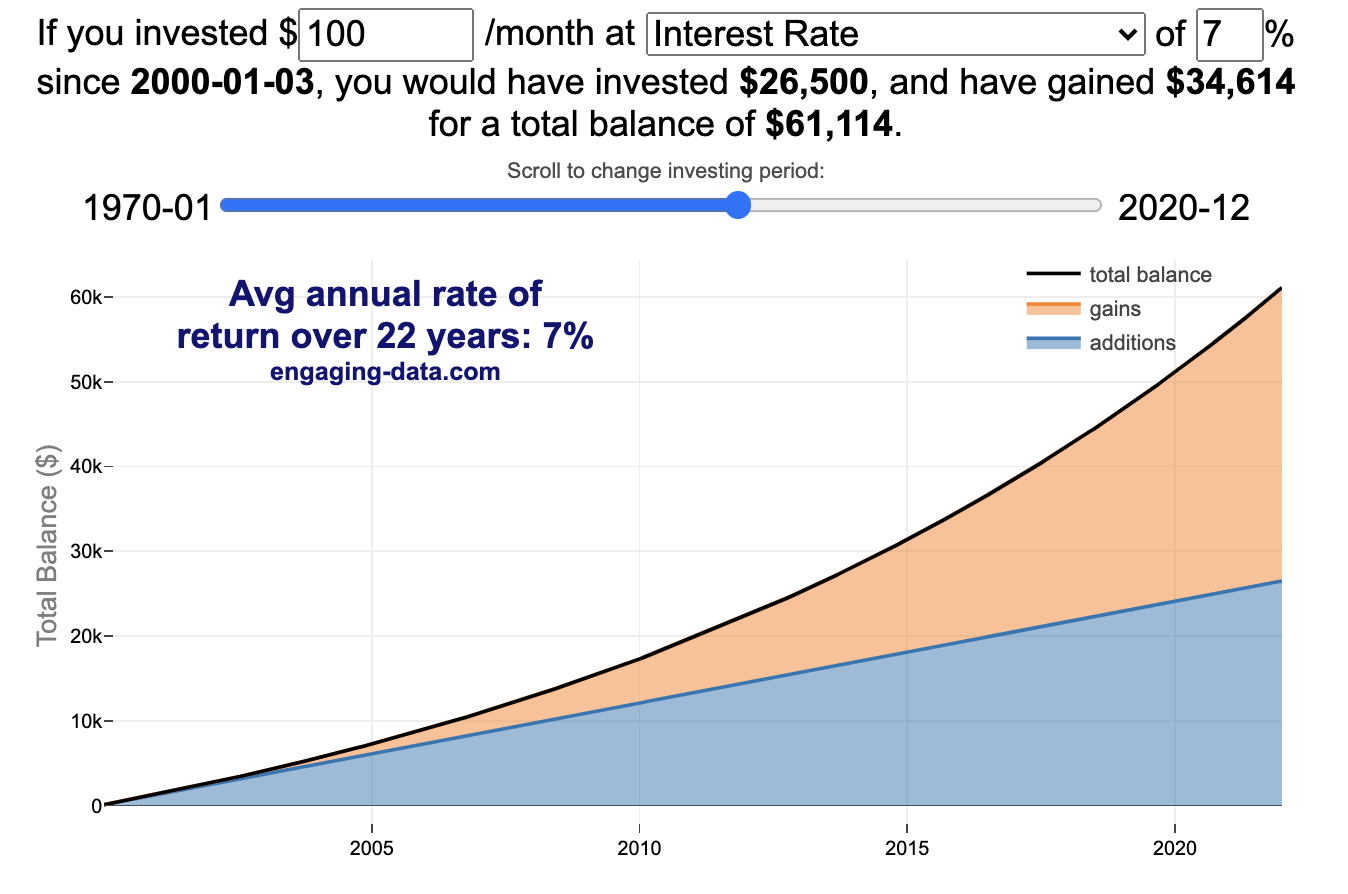
Calculating Returns from Periodic Investments
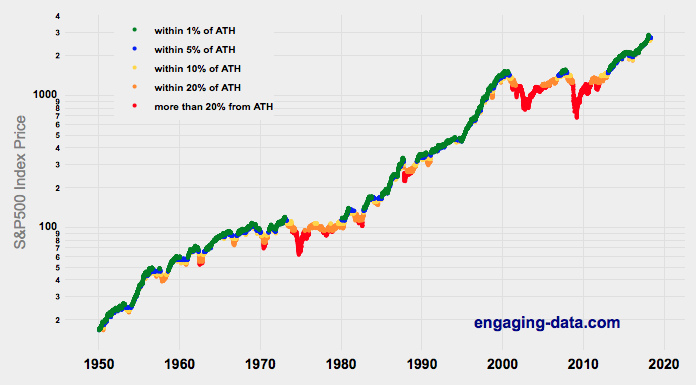
Visualizing Market Returns
Understanding Market Timing
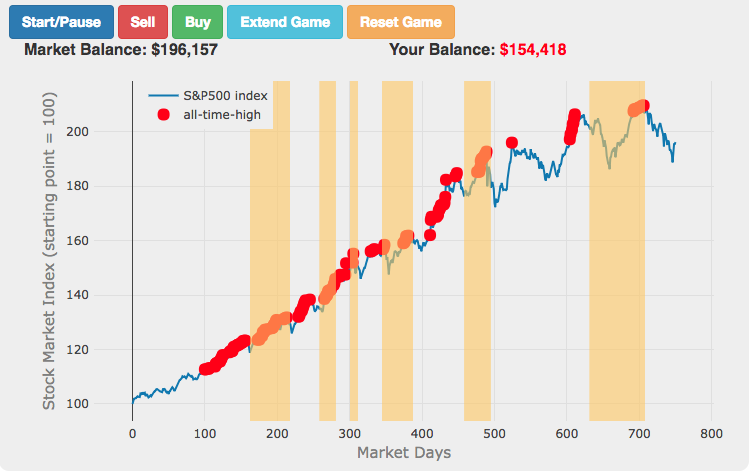
Market Timing Game
How difficult is it to time the stock market?
Income Taxes

Income Tax Bracket Calculator
Tax bracket calculator to visualize how income and capital gains taxed
Data Sources and Tools:
See the individual tool to learn more about how it was made.
How Much Does Each State Pay In Taxes?
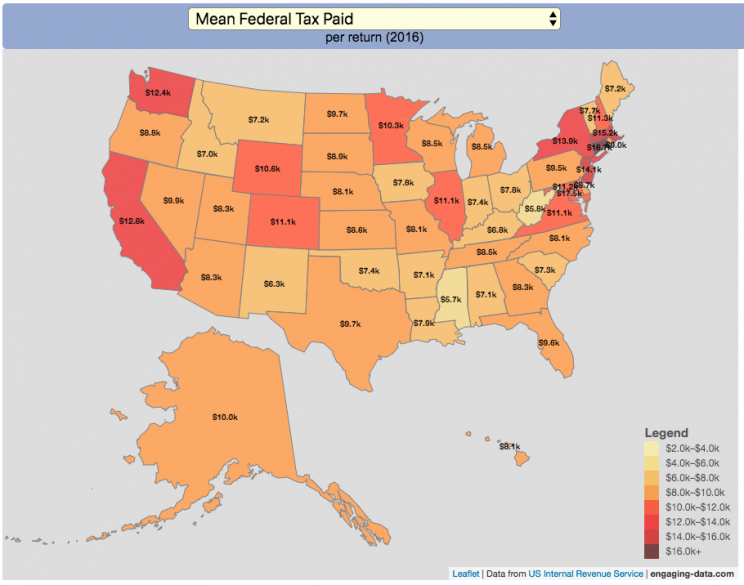
Given that tax day has just passed, I thought it would be good to check out some data on taxes. The IRS provides a great resource on tax data that I’ve only just gotten into. I think I’ll be able to do more with this in the future. This one looks at how taxes paid varies by state and presents it as a choropleth map (coloring states based on certain categories of tax data).
You can choose from a number of different categories:
- Mean Federal Tax Paid
- Mean Adjusted Gross Income
- Mean State/Local Tax
- Mean Combined (Fed/State/Local) Tax
- Percent Income from Dividends and Capital Gains
- Percent of Returns with Itemized Deductions
- Number of Tax Returns
- Mean Federal Tax Rate
- Mean State/Local Tax Rate
- Mean Combined (Fed/State/Local) Rate
- Total Federal Tax Liability
I may add more categories in the future, so if you have ideas of tax data you want to see visualized let me know and I’ll see what I can do.
For other tax-related tools and visualizations see my tax bracket calculator and visualization of marginal tax rates.
**Click Here to view other financial-related tools and data visualizations from engaging-data**
Data and Tools:
Data on tax returns by state is from the IRS website in an excel format. The map was made using the leaflet open source mapping library. Data was compiled in excel and calculations made using javascript.
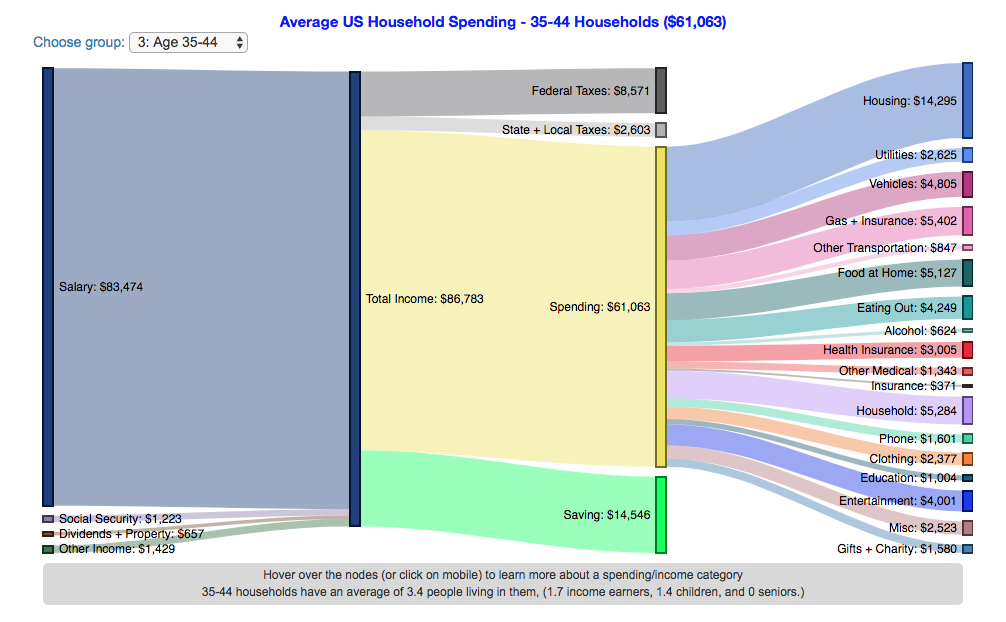
How do Americans Spend Money? US Household Spending Breakdown by Age
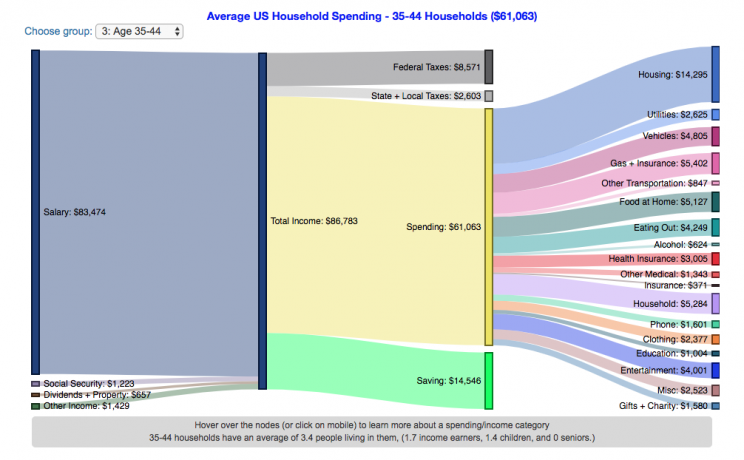
How much do US households spend and how does it change with age?
This visualization is one of a series of visualizations that present US household spending data from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics. This one looks at the age of the primary resident.
- US Household spending by income group
- US Household spending by age of primary resident
- US Household spending by education level of primary resident
- US Household spending by household composition
This visualization focuses on the age of the primary resident. This is defined in the BLS documentation as the person who is first mentioned when the survey respondent is asked who in the household rents or owns the home.
I obtained data from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), based upon a survey of consumer households and their spending habits. This data breaks down spending and income into many categories that are aggregated and plotted in a Sankey graph.
One of the key factors in financial health of an individual or household is making sure that household spending is equal to or below household income. If your spending is higher than income, you will be drawing down your savings (if you have any) or borrowing money. If your spending is lower than your income, you will presumably be saving money which can provide flexibility in the future, fund your retirement (maybe even early) and generally give you peace of mind.
Instructions:
- Hover (or on mobile click) on a link to get more information on the definition of a particular spending or income category.
- Use the dropdown menu to look at averages for different groups of households based on the age of the primary resident. This data breaks households into groups (under 25, 25-34, 35-44, 45-54, 55-64, 65-75 and over 75). The composition of households and income change as the age of the primary resident changes, which in turn affects spending totals and individual categories.
As stated before, one of the keys to financial security is spending less than your income. We can see that on average, income tends to increase with the household primary age up to the 45-54 group, then declines from there.
The youngest group (under 25) tends to borrow or draw down on savings to live their lifestyle, while the same is true of the over 75 age group. This is probably because seniors tend to draw down savings that were built up specifically for this purpose, and college students borrow to go to school. Social security also makes up a big portion of income for the older age groups.
How does your overall spending compare with those in your income group? How about spending in individual categories like housing, vehicles, food, clothing, etc…?
Probably one of the best things you can do from a financial perspective is to go through your spending and understand where your money is going. These sankey diagrams are one way to do it and see it visually, but of course, you can just make a table or pie chart or whatever.
The main thing is to understand where your money is going. Once you’ve done this you can be more conscious of what you are spending your money on, and then decide if you are spending too much (or too little) in certain categories. Having context of what other people spend money on is helpful as well, and why it is useful to compare to these averages, even though the income level, regional cost of living, and household composition won’t look exactly the same as your household.
**Click Here to view other financial-related tools and data visualizations from engaging-data**
Here is more information about the Consumer Expenditure Surveys from the BLS website:
The Consumer Expenditure Surveys (CE) collect information from the US households and families on their spending habits (expenditures), income, and household characteristics. The strength of the surveys is that it allows data users to relate the expenditures and income of consumers to the characteristics of those consumers. The surveys consist of two components, a quarterly Interview Survey and a weekly Diary Survey, each with its own questionnaire and sample.
Data and Tools:
Data on consumer spending was obtained from the BLS Consumer Expenditure Surveys, and aggregation and calculations were done using javascript and code modified from the Sankeymatic plotting website. I aggregated many of the survey output categories so as to make the graph legible, otherwise there’d be 4x as many spending categories and all very small and difficult to read.
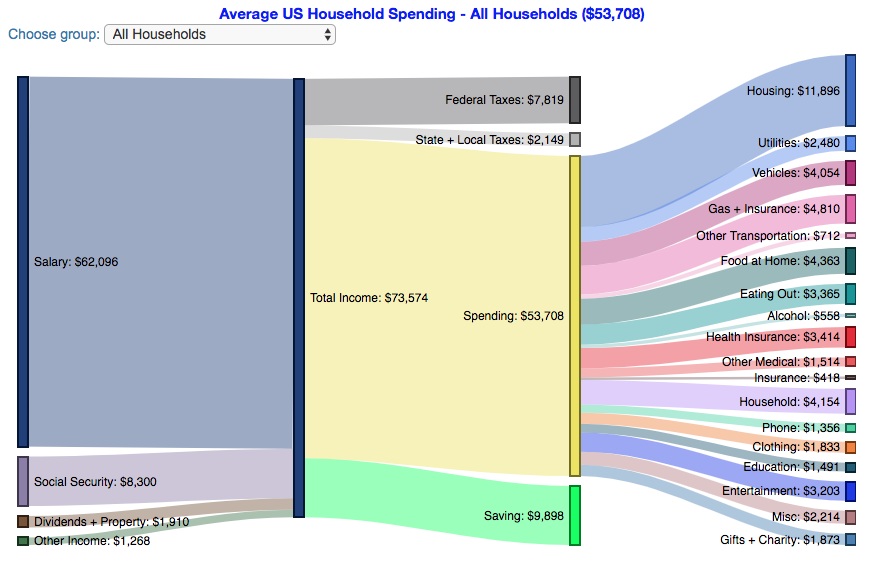
How do Americans Spend Money? US Household Spending Breakdown by Income Group
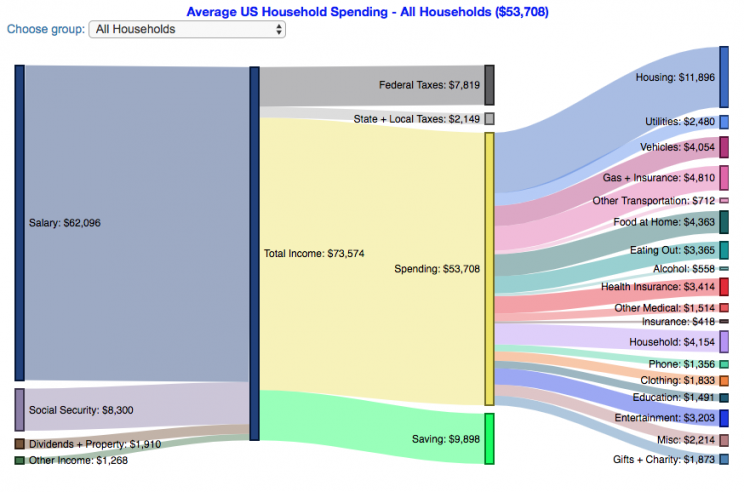
How much do US households spend?
This visualization is one of a series of visualizations that present US household spending data from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics. This one looks at the income of the household.
- US Household spending by income group
- US Household spending by age of primary resident
- US Household spending by education level of primary resident
- US Household spending by household composition
One of the key factors in financial health of an individual or household is making sure that household spending is equal to or below household income. If your spending is higher than income, you will be drawing down your savings (if you have any) or borrowing money. If your spending is lower than your income, you will presumably be saving money which can provide flexibility in the future, fund your retirement (maybe even early) and generally give you peace of mind.
I obtained data from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), based upon a survey of consumer households and their spending habits. This data breaks down spending and income into many categories that are aggregated and plotted in a Sankey graph.
Instructions:
- Hover (or on mobile click) on a link to get more information on the definition of a particular spending or income category.
- Use the dropdown menu to look at averages for different groups of households based on income. This data breaks households into quintiles (groups of 20%) by income. The lowest quintile group is the group of 20% of households with the lowest income (and spend on average ~$25,500/yr).
As stated before, one of the keys to financial security is spending less than your income. We can see that on average, those in the lowest quintiles may be borrowing or drawing down on savings to live their lifestyle, while those in the highest quintiles are saving money and contributing to wealth. This fairly high level of borrowing/drawing on savings from the lowest quintile households may be deceptive because it includes seniors who are drawing down savings that were built up specifically for this purpose, and college students who are borrowing to go to school. These groups generally don’t have significant incomes.
How does your overall spending compare with those in your income group? How about spending in individual categories like housing, vehicles, food, clothing, etc…?
Probably one of the best things you can do from a financial perspective is to go through your spending and understand where your money is going. These sankey diagrams are one way to do it and see it visually, but of course, you can just make a table or pie chart or whatever.
The main thing is to understand where your money is going. Once you’ve done this you can be more conscious of what you are spending your money on, and then decide if you are spending too much (or too little) in certain categories. Having context of what other people spend money on is helpful as well, and why it is useful to compare to these averages, even though the income level, regional cost of living, and household composition won’t look exactly the same as your household.
**Click Here to view other financial-related tools and data visualizations from engaging-data**
Here is more information about the Consumer Expenditure Surveys from the BLS website:
The Consumer Expenditure Surveys (CE) collect information from the US households and families on their spending habits (expenditures), income, and household characteristics. The strength of the surveys is that it allows data users to relate the expenditures and income of consumers to the characteristics of those consumers. The surveys consist of two components, a quarterly Interview Survey and a weekly Diary Survey, each with its own questionnaire and sample.
Data and Tools:
Data on consumer spending was obtained from the BLS Consumer Expenditure Surveys, and aggregation and calculations were done using javascript and code modified from the Sankeymatic plotting website. I aggregated many of the survey output categories so as to make the graph legible, otherwise there’d be 4x as many spending categories and all very small and difficult to read.
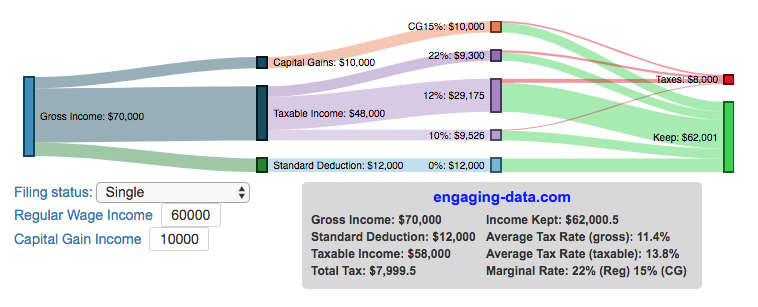
Tax Brackets v2.0: Interactive Income Tax Visualization and Calculator
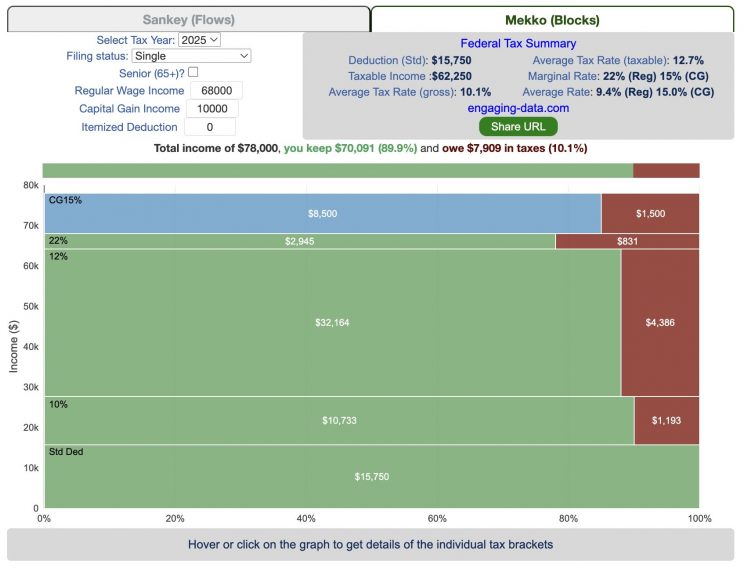
How is your income distributed across tax brackets?
This updated visualization is a detailed look at the breakdown how taxes are applied to your income across each of the tax brackets. The previous version of this visualization was a Sankey graph and this new version combines the sankey view with a mekko (or marimekko) graph view. It should help you to better understand marginal and average tax rates. This tool only looks at US Federal Income taxes and ignores state, local and Social Security/Medicare taxes.
**Click Here to view other financial-related tools and data visualizations from engaging-data**
Instructions for using the visual tax calculator:
- Tax Year: Select year from list of years as bracket sizes and deduction changes by year
- Select filing status: Single, Married Filing Jointly or Head of Household. For more info on these filing categories see the IRS website
- Senior checkbox Seniors are eligible for additional standard deduction and from 2025-2028 eligible for additional deduction even if you itemize
- Enter your regular income and capital gains income. Regular income is wage or employment income and is taxed at a higher rate than capital gains income. Capital gains income is typically investment income from the sale of stocks or dividends and taxed at a lower rate than regular income.
- Move your cursor or click on the Sankey graph to select a specific link. This will give you more information about how income in a specific tax bracket is being taxed.
- Itemized deduction Enter the amount of itemized deductions you have including: state and local (property) taxes, mortgage interest, charitable contributions and medical expenses above 7.5% of your AGI
- Share URL Click on the share button to generate a custom URL that will share a graph with your specific numbers in it. The link is copied to your clipboard and placed into the URL bar.
Interpreting the tax visualization graphs
Both the sankey and mekko graphs help you easily the size each of these tax brackets and the fraction of income in that bracket that you can keep and the fraction going to taxes. Also shown is the split of the regular income vs capital gains and how capital gains is “stacked” on top of the regular income.
The mekko graph is a stacked horizontal bar graph where the height of each bar is proportional to the size of the tax bracket and the bar is split into two parts: a keep and a tax portion. This makes it clear the progressive nature of the tax code, initial tax brackets are taxed at the lowest amounts and as you fill up more tax brackets, the tax rate, and the amount of money you must give to the government, increases.
As seen with the marginal rates graph, there is a big difference in how regular income and capital gains are taxed. Capital gains are taxed at a lower rate and generally have larger bracket sizes. Generally, wealthier households earn a greater fraction of their income from capital gains and as a result of the lower tax rates on capital gains, these household pay a lower effective tax rate than those making an order of magnitude less in overall income.
Also shown is a summary bar graph that shows the split in your total income into a part that you keep and the other that owed to taxes, i.e. your average tax rate.
How Do Tax Brackets Work
This is a written description of how to apply marginal tax rates. The income you have is split across various tax brackets, which by analogy can be thought of as buckets where once you fill one up, the additional money goes into another bucket, until that is filled up and so on until all your income is distributed across these brackets. The last brackets are open-ended so they are of infinite size.
You start with your deductions which changes based on your filing status, age and if you have itemized deductions. You fill this up first and you can think of this as the 0% tax bracket. Then any additional income goes into the 10% bracket where 10% of this income goes to taxes. This proceeds then onto the 12%, 22% and so on brackets.
The default example is described here for tax year 2025
- If you are single, your standard deduction is $15,750 and you pay no taxes on this money. After that, all of your regular taxable income up to $11,925 is taxed at a 10% rate. This means that your all of your gross income below $15,750 is not taxed and your gross income between $15,750 and $27,675 is taxed at 10%.
- If you have more income, you move up a marginal tax bracket. The next $36,550 in additional taxable income will be taxed at the 12% rate. It is important to note that not all of your income is taxed at the marginal rate, just the income in this bracket these amounts.
- The next $48,900 is taxed at 22% and so on until you have income over $500,000 and are in the 37% marginal tax rate . . . In the default case, you only have $3,775 instead of $48,900 so this portion is taxed at 22%.
- Thus, different parts of your income are taxed at different rates. If you have additional income that puts you into a higher tax bracket, that only affects the added income. This is the approach you would use to calculate an average or effective rate (which is shown in the summary table).
- Capital gains income complicates things slightly as it is taxed after regular income. Thus any amount of capital gains taxes you make are taxed at a rate that corresponds to starting after you regular income. If you made $100,000 in regular income, and only $100 in capital gains income, that $100 dollars would be taxed at the 15% rate and not at the 0% rate, because the $100,000 in regular income pushes you into the 2nd marginal tax bracket for capital gains (between $48,350 and $533,400).
- if the 0% capital gains rate threshold is at $48,350, then any regular income you have will take away from this 0% bracket size. If you have $48,000 in regular taxable income after your deduction, then you will be left with only $350 in 0% capital gains bracket space and the remainder of your capital gains will be taxed in the next bracket, 15%.
Tax Brackets By Year
This table lets you choose to view the thresholds for each income and capital gains tax bracket for the last few years. You can see that tax rates are much lower for capital gains in the table below than for regular income.
Data and Tools:
Tax brackets and rates were obtained from the IRS website and calculations were made using javascript, CSS and HTML. The sankey graph was made using code modified from the Sankeymatic plotting website and the mekko graph was made using the Plotly javascript open source library.

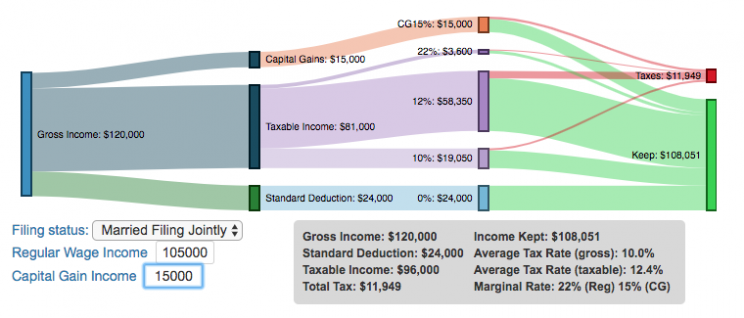
Understanding Tax Brackets: Interactive Income Tax Visualization and Calculator

Please check out the newer version of this visualization 
How is your income distributed across tax brackets?
I previously made a graphical visualization of income and marginal tax rates to show how tax brackets work. That graph tried to show alot of info on the same graph, i.e. the breakdown of income tax brackets for incomes ranging from $10,000 to $3,000,000. It was nice looking, but I think several people were confused about how to read the graph. This Sankey graph is a more detailed look at the tax breakdown for one specific income. You can enter your (or any other) profile and see how taxes are distributed across the different brackets. It can help (as the other tried) to better understand marginal and average tax rates. This tool only looks at US Federal Income taxes and ignores state, local and Social Security/Medicare taxes.
– Use this button to generate a URL that you can share a specific set of inputs and graphs. Just copy the URL in the address bar at the top of your browser (after pressing the button).
- Select filing status: Single, Married Filing Jointly or Head of Household. For more info on these filing categories see the IRS website
- Enter your regular income and capital gains income. Regular income is wage or employment income and is taxed at a higher rate than capital gains income. Capital gains income is typically investment income from the sale of stocks or dividends and taxed at a lower rate than regular income.
- Move your cursor or click on the Sankey graph to select a specific link. This will give you more information about how income in a specific tax bracket is being taxed.
**Click Here to view other financial-related tools and data visualizations from engaging-data**
As seen with the marginal rates graph, there is a big difference in how regular income and capital gains are taxed. Capital gains are taxed at a lower rate and generally have larger bracket sizes. Generally, wealthier households earn a greater fraction of their income from capital gains and as a result of the lower tax rates on capital gains, these household pay a lower effective tax rate than those making an order of magnitude less in overall income.
Tax Brackets By Year
This table lets you choose to view the thresholds for each income and capital gains tax bracket for the last few years. You can see that tax rates are much lower for capital gains in the table below than for regular income.
- If you are single, all of your regular taxable income between 0 and $9,525 is taxed at a 10% rate. This means that your all of your gross income below $12,000 is not taxed and your gross income between $12,000 and $21,525 is taxed at 10%.
- If you have more income, you move up a marginal tax bracket. Any taxable income in excess of $9,525 but below $38,700 will be taxed at the 12% rate. It is important to note that not all of your income is taxed at the marginal rate, just the income between these amounts.
- Income between $38,700 and $82,500 is taxed at 24% and so on until you have income over $500,000 and are in the 37% marginal tax rate . . .
- Thus, different parts of your income are taxed at different rates and you can calculate an average or effective rate (which is shown in the summary table).
- Capital gains income complicates things slightly as it is taxed after regular income. Thus any amount of capital gains taxes you make are taxed at a rate that corresponds to starting after you regular income. If you made $100,000 in regular income, and only $100 in capital gains income, that $100 dollars would be taxed at the 15% rate and not at the 0% rate, because the $100,000 in regular income pushes you into the 2nd marginal tax bracket for capital gains (between $38,700 and $426,700).
Data and Tools:
Tax brackets and rates were obtained from the IRS website and calculations were made using javascript and code modified from the Sankeymatic plotting website.

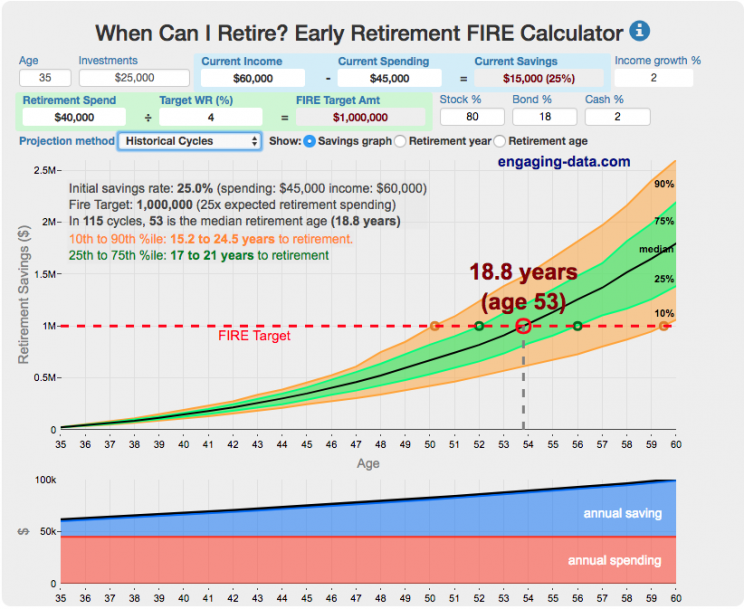
Early Retirement Calculators and Tools

Interested in Early Retirement or FIRE (Financial Independence to Retire Early)?
Here are some interactive and educational planning tools that I developed to help you understand the concepts of FIRE and calculate how long it will take to achieve retirement and how likely you are to survive retirement. Click on the tools below to try them out.
Financial Independence Calculators
Regardless of where you are on your path to FIRE, there are several types of tools that are useful:
Planning to get to retirement
How long and how safe will your retirement be?

Rich, Broke or Dead? Will your Money Last Through Early Retirement?
Simulating retirement portfolio survival probability and human longevity
These tools all focus on the concept of FIRE. FIRE is the concept that revolves around saving and investing to achieve Financial Independence (FI) and to potentially Retire Early (RE). One of the core concepts is that once you can save up enough money, you can retire by withdrawing a fraction of this money annually to cover your living expenses. Other important topics related to this core concept have to do with reducing spending so you can save money and investing so your money can grow and sustain your retirement over many decades.
Other visualizations and tools related to Financial Independence
These tools relate to taxes and stock market returns.
Calculating Returns from Periodic Investments
Visualizing Market Returns
Understanding Market Timing
How difficult is it to time the stock market?

Market Timing Game
Income Taxes
Tax bracket calculator to visualize how income and capital gains taxed

Income Tax Bracket Calculator
Data Sources and Tools:
See the individual tool to learn more about how it was made.
How Much Does Each State Pay In Taxes?

Given that tax day has just passed, I thought it would be good to check out some data on taxes. The IRS provides a great resource on tax data that I’ve only just gotten into. I think I’ll be able to do more with this in the future. This one looks at how taxes paid varies by state and presents it as a choropleth map (coloring states based on certain categories of tax data).
- Mean Federal Tax Paid
- Mean Adjusted Gross Income
- Mean State/Local Tax
- Mean Combined (Fed/State/Local) Tax
- Percent Income from Dividends and Capital Gains
- Percent of Returns with Itemized Deductions
- Number of Tax Returns
- Mean Federal Tax Rate
- Mean State/Local Tax Rate
- Mean Combined (Fed/State/Local) Rate
- Total Federal Tax Liability
I may add more categories in the future, so if you have ideas of tax data you want to see visualized let me know and I’ll see what I can do.
For other tax-related tools and visualizations see my tax bracket calculator and visualization of marginal tax rates.
**Click Here to view other financial-related tools and data visualizations from engaging-data**
Data and Tools:
Data on tax returns by state is from the IRS website in an excel format. The map was made using the leaflet open source mapping library. Data was compiled in excel and calculations made using javascript.

How do Americans Spend Money? US Household Spending Breakdown by Age

How much do US households spend and how does it change with age?
This visualization is one of a series of visualizations that present US household spending data from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics. This one looks at the age of the primary resident.
- US Household spending by income group
- US Household spending by age of primary resident
- US Household spending by education level of primary resident
- US Household spending by household composition
This visualization focuses on the age of the primary resident. This is defined in the BLS documentation as the person who is first mentioned when the survey respondent is asked who in the household rents or owns the home.
I obtained data from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), based upon a survey of consumer households and their spending habits. This data breaks down spending and income into many categories that are aggregated and plotted in a Sankey graph.
One of the key factors in financial health of an individual or household is making sure that household spending is equal to or below household income. If your spending is higher than income, you will be drawing down your savings (if you have any) or borrowing money. If your spending is lower than your income, you will presumably be saving money which can provide flexibility in the future, fund your retirement (maybe even early) and generally give you peace of mind.
Instructions:
- Hover (or on mobile click) on a link to get more information on the definition of a particular spending or income category.
- Use the dropdown menu to look at averages for different groups of households based on the age of the primary resident. This data breaks households into groups (under 25, 25-34, 35-44, 45-54, 55-64, 65-75 and over 75). The composition of households and income change as the age of the primary resident changes, which in turn affects spending totals and individual categories.
As stated before, one of the keys to financial security is spending less than your income. We can see that on average, income tends to increase with the household primary age up to the 45-54 group, then declines from there.
The youngest group (under 25) tends to borrow or draw down on savings to live their lifestyle, while the same is true of the over 75 age group. This is probably because seniors tend to draw down savings that were built up specifically for this purpose, and college students borrow to go to school. Social security also makes up a big portion of income for the older age groups.
How does your overall spending compare with those in your income group? How about spending in individual categories like housing, vehicles, food, clothing, etc…?
Probably one of the best things you can do from a financial perspective is to go through your spending and understand where your money is going. These sankey diagrams are one way to do it and see it visually, but of course, you can just make a table or pie chart or whatever.
The main thing is to understand where your money is going. Once you’ve done this you can be more conscious of what you are spending your money on, and then decide if you are spending too much (or too little) in certain categories. Having context of what other people spend money on is helpful as well, and why it is useful to compare to these averages, even though the income level, regional cost of living, and household composition won’t look exactly the same as your household.
**Click Here to view other financial-related tools and data visualizations from engaging-data**
Here is more information about the Consumer Expenditure Surveys from the BLS website:
The Consumer Expenditure Surveys (CE) collect information from the US households and families on their spending habits (expenditures), income, and household characteristics. The strength of the surveys is that it allows data users to relate the expenditures and income of consumers to the characteristics of those consumers. The surveys consist of two components, a quarterly Interview Survey and a weekly Diary Survey, each with its own questionnaire and sample.
Data and Tools:
Data on consumer spending was obtained from the BLS Consumer Expenditure Surveys, and aggregation and calculations were done using javascript and code modified from the Sankeymatic plotting website. I aggregated many of the survey output categories so as to make the graph legible, otherwise there’d be 4x as many spending categories and all very small and difficult to read.

How do Americans Spend Money? US Household Spending Breakdown by Income Group

How much do US households spend?
This visualization is one of a series of visualizations that present US household spending data from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics. This one looks at the income of the household.
- US Household spending by income group
- US Household spending by age of primary resident
- US Household spending by education level of primary resident
- US Household spending by household composition
One of the key factors in financial health of an individual or household is making sure that household spending is equal to or below household income. If your spending is higher than income, you will be drawing down your savings (if you have any) or borrowing money. If your spending is lower than your income, you will presumably be saving money which can provide flexibility in the future, fund your retirement (maybe even early) and generally give you peace of mind.
I obtained data from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), based upon a survey of consumer households and their spending habits. This data breaks down spending and income into many categories that are aggregated and plotted in a Sankey graph.
Instructions:
- Hover (or on mobile click) on a link to get more information on the definition of a particular spending or income category.
- Use the dropdown menu to look at averages for different groups of households based on income. This data breaks households into quintiles (groups of 20%) by income. The lowest quintile group is the group of 20% of households with the lowest income (and spend on average ~$25,500/yr).
As stated before, one of the keys to financial security is spending less than your income. We can see that on average, those in the lowest quintiles may be borrowing or drawing down on savings to live their lifestyle, while those in the highest quintiles are saving money and contributing to wealth. This fairly high level of borrowing/drawing on savings from the lowest quintile households may be deceptive because it includes seniors who are drawing down savings that were built up specifically for this purpose, and college students who are borrowing to go to school. These groups generally don’t have significant incomes.
How does your overall spending compare with those in your income group? How about spending in individual categories like housing, vehicles, food, clothing, etc…?
Probably one of the best things you can do from a financial perspective is to go through your spending and understand where your money is going. These sankey diagrams are one way to do it and see it visually, but of course, you can just make a table or pie chart or whatever.
The main thing is to understand where your money is going. Once you’ve done this you can be more conscious of what you are spending your money on, and then decide if you are spending too much (or too little) in certain categories. Having context of what other people spend money on is helpful as well, and why it is useful to compare to these averages, even though the income level, regional cost of living, and household composition won’t look exactly the same as your household.
**Click Here to view other financial-related tools and data visualizations from engaging-data**
Here is more information about the Consumer Expenditure Surveys from the BLS website:
The Consumer Expenditure Surveys (CE) collect information from the US households and families on their spending habits (expenditures), income, and household characteristics. The strength of the surveys is that it allows data users to relate the expenditures and income of consumers to the characteristics of those consumers. The surveys consist of two components, a quarterly Interview Survey and a weekly Diary Survey, each with its own questionnaire and sample.
Data and Tools:
Data on consumer spending was obtained from the BLS Consumer Expenditure Surveys, and aggregation and calculations were done using javascript and code modified from the Sankeymatic plotting website. I aggregated many of the survey output categories so as to make the graph legible, otherwise there’d be 4x as many spending categories and all very small and difficult to read.

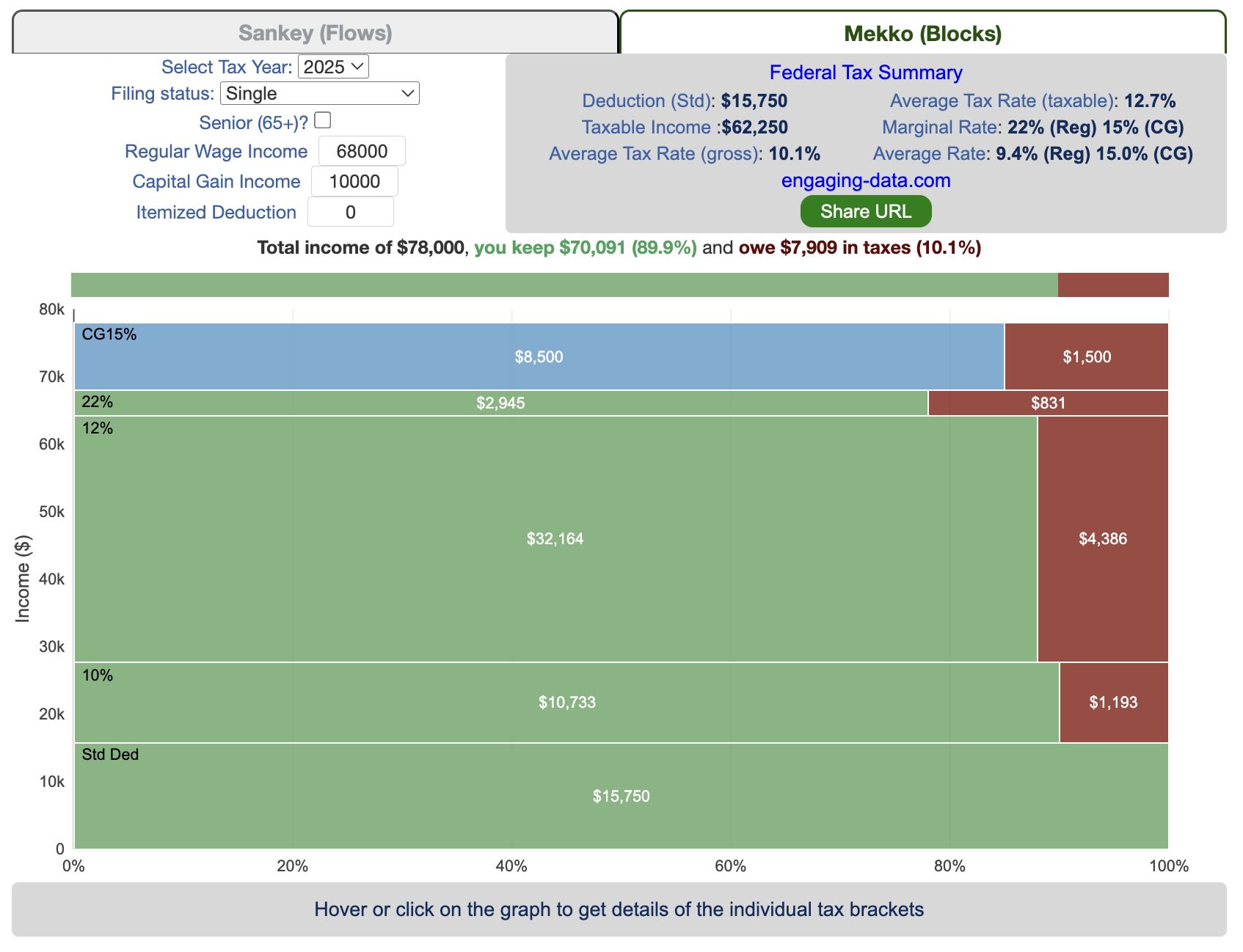
Tax Brackets v2.0: Interactive Income Tax Visualization and Calculator

How is your income distributed across tax brackets?
This updated visualization is a detailed look at the breakdown how taxes are applied to your income across each of the tax brackets. The previous version of this visualization was a Sankey graph and this new version combines the sankey view with a mekko (or marimekko) graph view. It should help you to better understand marginal and average tax rates. This tool only looks at US Federal Income taxes and ignores state, local and Social Security/Medicare taxes.
**Click Here to view other financial-related tools and data visualizations from engaging-data**
Instructions for using the visual tax calculator:
- Tax Year: Select year from list of years as bracket sizes and deduction changes by year
- Select filing status: Single, Married Filing Jointly or Head of Household. For more info on these filing categories see the IRS website
- Senior checkbox Seniors are eligible for additional standard deduction and from 2025-2028 eligible for additional deduction even if you itemize
- Enter your regular income and capital gains income. Regular income is wage or employment income and is taxed at a higher rate than capital gains income. Capital gains income is typically investment income from the sale of stocks or dividends and taxed at a lower rate than regular income.
- Move your cursor or click on the Sankey graph to select a specific link. This will give you more information about how income in a specific tax bracket is being taxed.
- Itemized deduction Enter the amount of itemized deductions you have including: state and local (property) taxes, mortgage interest, charitable contributions and medical expenses above 7.5% of your AGI
- Share URL Click on the share button to generate a custom URL that will share a graph with your specific numbers in it. The link is copied to your clipboard and placed into the URL bar.
Interpreting the tax visualization graphs
Both the sankey and mekko graphs help you easily the size each of these tax brackets and the fraction of income in that bracket that you can keep and the fraction going to taxes. Also shown is the split of the regular income vs capital gains and how capital gains is “stacked” on top of the regular income.
The mekko graph is a stacked horizontal bar graph where the height of each bar is proportional to the size of the tax bracket and the bar is split into two parts: a keep and a tax portion. This makes it clear the progressive nature of the tax code, initial tax brackets are taxed at the lowest amounts and as you fill up more tax brackets, the tax rate, and the amount of money you must give to the government, increases.
As seen with the marginal rates graph, there is a big difference in how regular income and capital gains are taxed. Capital gains are taxed at a lower rate and generally have larger bracket sizes. Generally, wealthier households earn a greater fraction of their income from capital gains and as a result of the lower tax rates on capital gains, these household pay a lower effective tax rate than those making an order of magnitude less in overall income.
Also shown is a summary bar graph that shows the split in your total income into a part that you keep and the other that owed to taxes, i.e. your average tax rate.
How Do Tax Brackets Work
This is a written description of how to apply marginal tax rates. The income you have is split across various tax brackets, which by analogy can be thought of as buckets where once you fill one up, the additional money goes into another bucket, until that is filled up and so on until all your income is distributed across these brackets. The last brackets are open-ended so they are of infinite size.
You start with your deductions which changes based on your filing status, age and if you have itemized deductions. You fill this up first and you can think of this as the 0% tax bracket. Then any additional income goes into the 10% bracket where 10% of this income goes to taxes. This proceeds then onto the 12%, 22% and so on brackets.
The default example is described here for tax year 2025
- If you are single, your standard deduction is $15,750 and you pay no taxes on this money. After that, all of your regular taxable income up to $11,925 is taxed at a 10% rate. This means that your all of your gross income below $15,750 is not taxed and your gross income between $15,750 and $27,675 is taxed at 10%.
- If you have more income, you move up a marginal tax bracket. The next $36,550 in additional taxable income will be taxed at the 12% rate. It is important to note that not all of your income is taxed at the marginal rate, just the income in this bracket these amounts.
- The next $48,900 is taxed at 22% and so on until you have income over $500,000 and are in the 37% marginal tax rate . . . In the default case, you only have $3,775 instead of $48,900 so this portion is taxed at 22%.
- Thus, different parts of your income are taxed at different rates. If you have additional income that puts you into a higher tax bracket, that only affects the added income. This is the approach you would use to calculate an average or effective rate (which is shown in the summary table).
- Capital gains income complicates things slightly as it is taxed after regular income. Thus any amount of capital gains taxes you make are taxed at a rate that corresponds to starting after you regular income. If you made $100,000 in regular income, and only $100 in capital gains income, that $100 dollars would be taxed at the 15% rate and not at the 0% rate, because the $100,000 in regular income pushes you into the 2nd marginal tax bracket for capital gains (between $48,350 and $533,400).
- if the 0% capital gains rate threshold is at $48,350, then any regular income you have will take away from this 0% bracket size. If you have $48,000 in regular taxable income after your deduction, then you will be left with only $350 in 0% capital gains bracket space and the remainder of your capital gains will be taxed in the next bracket, 15%.
Tax Brackets By Year
This table lets you choose to view the thresholds for each income and capital gains tax bracket for the last few years. You can see that tax rates are much lower for capital gains in the table below than for regular income.
Data and Tools:
Tax brackets and rates were obtained from the IRS website and calculations were made using javascript, CSS and HTML. The sankey graph was made using code modified from the Sankeymatic plotting website and the mekko graph was made using the Plotly javascript open source library.

Recent Comments